6.1 KiB
prim-dns server script
The prim-dns server script is a modular SecondLife script that will request a temporary URL and register that URL with a prim-dns web service instance to automatically create a permanent alias, which client scripts can use to find the current temporary URL of the server at any given time. This allows you to quickly add robust HTTP server functionality to any prim, and the modular design means the core script can be updated without needing to edit your own code, and different functions of a server can be split across multiple scripts for easier management.
You can grab the core prim-dns script along with several examples here.
A working version of the example file server can be viewed here.
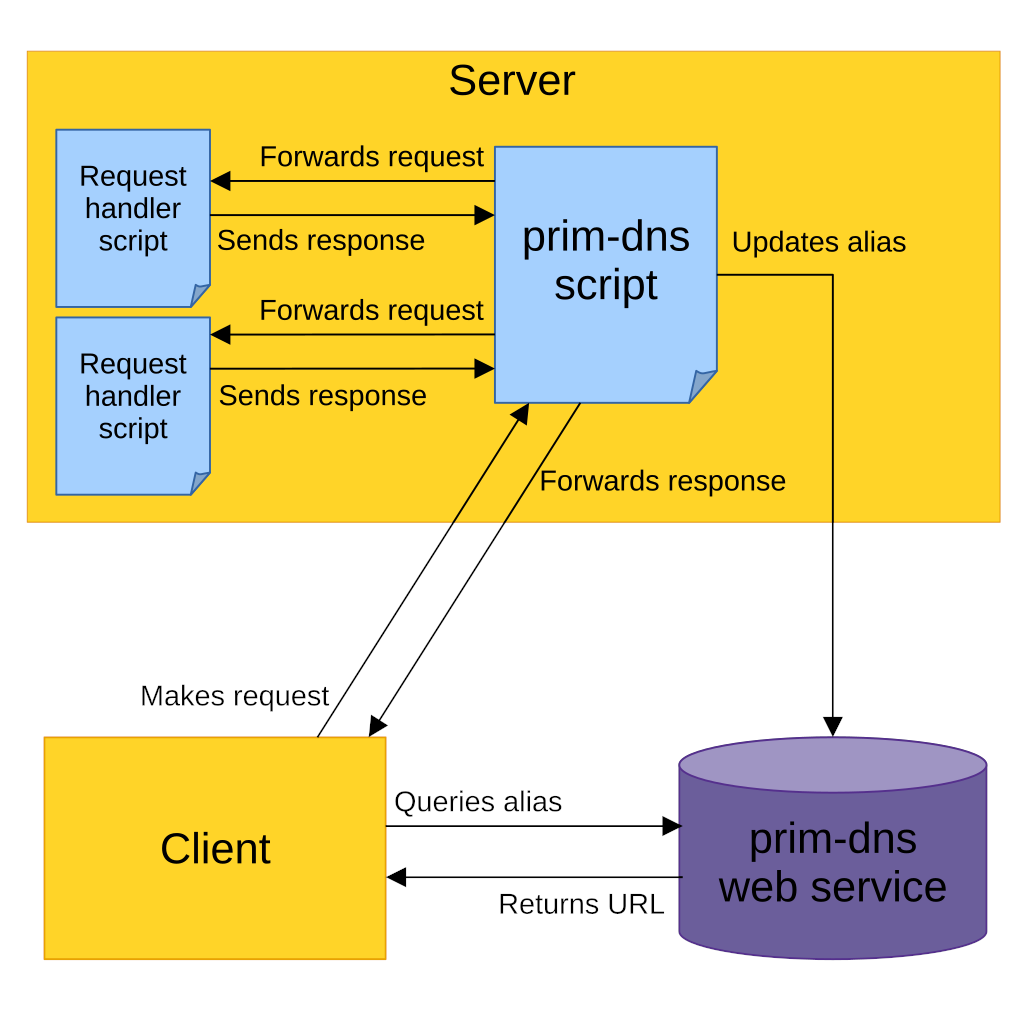
prim-dns server diagram
The diagram below illustrates the communication between the prim-dns server script, the request handler scripts, the prim-dns web service, and a client.
Link messages API
Communication between the prim-dns script and the request handler scripts is accomplished via link messages, where the string portion of the message is a JSON-RPC object.
prim-dns:request (request-id, method, body)
The prim-dns script received an HTTP request.
Parameters
request-idThe key of the request.methodThe HTTP method of the request.bodyThe body of the request.
Example
link_message(integer sender, integer num, string str, key id)
{
if (llJsonGetValue(str, ["method"]) == "prim-dns:request")
{
key request_id = (key) llJsonGetValue(str, ["params", "request-id"]);
string params = llList2Json(JSON_OBJECT, [
"request-id", request_id,
"status", 200,
"body", "Hello, world!"
]);
string message = llList2Json(JSON_OBJECT, [
"method", "prim-dns:response",
"params", params
]);
llMessageLinked(sender, 0, message, NULL_KEY);
}
}
prim-dns:set-content-type (request-id, content-type)
Set the content type of the response.
Parameters
request-idThe key of the request to set the response content type for.content-typeOne of the supported content type constants.
Example
string params = llList2Json(JSON_OBJECT, [
"request-id", request_id,
"content-type", CONTENT_TYPE_HTML
]);
string message = llList2Json(JSON_OBJECT, [
"method", "prim-dns:set-content-type",
"params", params
]);
llMessageLinked(LINK_THIS, 0, message, NULL_KEY);
prim-dns:response (request-id, status, body)
Send the response.
Parameters
request-idThe key of the request to respond to.statusThe HTTP status code of the response.bodyThe body of the response.
Example
string params = llList2Json(JSON_OBJECT, [
"request-id", request_id,
"status", 200,
"body", "Hello, world!"
]);
string message = llList2son(JSON_OBJECT, [
"method", "prim-dns:response",
"params", params
]);
llMessageLinked(LINK_THIS, 0, message, NULL_KEY);
prim-dns:reboot ()
Reboot the prim-dns server.
Example
string message = llList2Json(JSON_OBJECT, [
"method", "prim-dns:reboot"
]);
llMessageLinked(LINK_THIS, 0, message, NULL_KEY);
prim-dns:shutdown ()
Shut down the prim-dns server.
Example
string message = llList2Json(JSON_OBJECT, [
"method", "prim-dns:shutdown"
]);
llMessageLinked(LINK_THIS, 0, message, NULL_KEY);
prim-dns:startup ()
Sent when the prim-dns server finishes reading the configuration and is waiting to continue starting up. If auto_start = 1, then the server will immediately continue, otherwise it will wait for the prim-dns:start messsage.
Example
link_message(integer sender, integer num, string str, key id)
{
if (llJsonGetValue(str, ["method"]) == "prim-dns:startup")
{
llOwnerSay("The prim-dns server is now waiting to start.");
}
}
prim-dns:start ()
Tell the prim-dns server to complete its startup.
Example
string message = llList2Json(JSON_OBJECT, [
"method", "prim-dns:start"
]);
llMessageLinked(LINK_THIS, 0, message, NULL_KEY);
prim-dns:url-request-granted (url)
Sent when the prim-dns server is granted a temporary URL by the region.
Parameters
urlThe temporary URL assigned to the script.
Example
link_message(integer sender, integer num, string str, key id)
{
if (llJsonGetValue(str, ["method"]) == "prim-dns:url-request-granted")
{
llOwnerSay("The prim-dns server was granted a URL: " + llJsonGetValue(str, ["params", "url"]));
}
}
prim-dns:alias-registered (alias)
Sent when the prim-dns server successfully registers or updates its alias.
Parameters
aliasThe endpoint URL of the registered alias.
Example
link_message(integer sender, integer num, string str, key id)
{
if (llJsonGetValue(str, ["method"]) == "prim-dns:alias-registered")
{
llOwnerSay("The alias was successfully registered: " + llJsonGetValue(str, ["params", "alias"]));
}
}
prim-dns:shutting-down ()
Sent when the prim-dns server is shutting down.
Example
link_message(integer sender, integer num, string str, key id)
{
if (llJsonGetValue(str, ["method"]) == "prim-dns:shutting-down")
{
llOwnerSay("The prim-dns server is shutting down.");
}
}
Known issues / Future improvements
- The amount of data you can send in a response is limited by the amount of memory available to the core prim-dns script. Therefore, this script needs to be as memory-efficient as possible, but without sacrificing the user interface.
- There could be a second script which actually requests URLs and handles requests and responses, and that script would have more memory to work with. However, it would also be necessary to use multiple prims in order to prevent the core script from receiving link messages that would exceed the memory available to it.